A blowout preventer (BOP) is a mechanical device used to seal an oil or gas well in the event of an uncontrolled fluid flow or release from the well to prevent a blowout. A BOP may be used to protect personnel and/or equipment during drilling. BOPs are subject to regular testing to ensure conformity with regulations. Typically, testing involves stopping drilling operations prior to reaching a target drilling depth and pulling the drill string back to the surface.
In July 2021, Aker Solutions Limited was granted UK patent GB2551100B titled Apparatus and method for testing a blowout preventer.
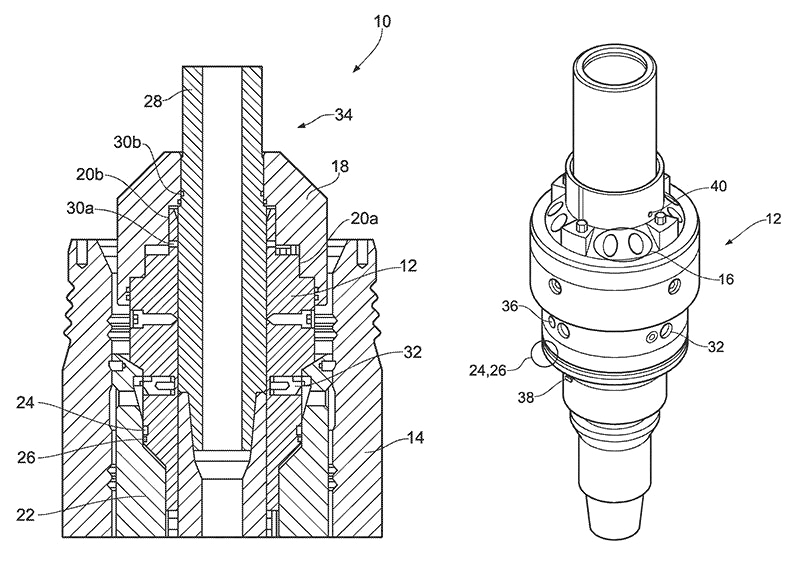
The patent discloses an apparatus (10) comprising a drilling tool (12), configured to be located and used in a wellhead (14) below a BOP – the drilling tool having fluid ports therein (16). The apparatus also includes a collar (18), the collar being mateable with the drilling tool. The fluid ports in the drilling tool are blocked by the collar when the collar is mated with the drilling tool below the BOP. The wellhead may be, for example, a subsea wellhead.
Optionally, surfaces of the collar and the drilling tool (20a, 20b) may be complementary such that the fluid ports in the drilling tool are readily blocked by the collar when the surfaces are mated together. The drilling tool may be sealed against a wear bushing (22) using seals (24, 26). The drilling tool may be a runnable drill string tool and the wear bushing may be a bit runnable wear bushing. The drilling tool and wear bushing may be attached to each other via spring loaded dogs (32). A mandrel (28) may be releasably attached to the drilling tool via shear pins (30a, 30b).
The patent also discloses a method of testing a BOP on a subsea wellhead, which includes locating the drilling tool in a wellhead below the BOP, the drilling tool having fluid ports therein; running a collar into the wellhead, the collar mating with the drilling tool; blocking the fluid ports in the drilling tool using the collar; and pumping a fluid into a chamber (34) between the BOP on the wellhead and the collar.
The drilling tool may have shear pins (36) which, like the spring loaded dogs, are used for running the wear bushing. The drilling tool may have an anti-rotation key (38) and a shear pin (40). The method may further include the step of pulling the drill string back a set distance, allowing the collar to be made up with the drill string before being run back into the wellhead.
In use, fluid may be pumped into the chamber to build up fluid pressure. The collar may be held onto the drilling tool such that it is mated with the drilling tool by the fluid pressure. During testing, a plug may be placed in the bore of the mandrel to block the fluid path. A BOP may be considered to have passed testing if the fluid remains in the chamber at the fluid pressure, which may be between 5,000-10,000psi.
The apparatus allows for the installation of a wear bushing, selectively retrieving the wear bushing, and testing a BOP in a subsea wellhead. The drilling tool and/or wear bushing can remain in the wellhead while the BOP is being tested. BOP testing may be performed in the same operation as running the bit runnable wear bushing. This may save time, especially in deep water, as the full drill string does not need to be recovered to the surface to perform a BOP test.
Read the full patent here.
This article first appeared in the September 2021 issue of Materials World, the member magazine of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining.
The Patent Eye blog offers a glimpse into the future by showcasing newly granted patents. Join us as we explore the latest innovations shaping our world.
The Patent Eye blog is made available by Alphabet Intellectual Property for informational purposes, in particular, sharing of newly patented technology from granted and published patents available in the public domain. It is not meant to convey legal position on behalf of any client, nor is it intended to convey specific legal advice.
Craving intellectual stimulus? Peer into the insights brought to you by The Patent Eye and explore our latest articles.